 de novo
de novo genome sequencing is used to sequence uncharacterized genomes where there is no reference sequence available, or known genomes where significant structural variation is expected. A detailed genetic analysis of an organism is possible only after de novo sequencing has been performed. To date, BGI Tech has sequenced 656 plant and animal reference genomes. The completed projects include rice, cucumber, potato, wheat, silkworm, panda, ant, oyster, minke whale, and so on.
Benefits:
- Best assembly quality with the highest N50 scaffold and contig sizes provided
- More comprehensive maps of genetic variation
- Variable gradient insert libraries that enable fine mapping of the genome

Comparative analysis of Fruit bat
Pteropus alecto and insectivorous
Myotis davidii genomes (~ 2 Gb) provides insight into the phylogenetic placement of bats, and moreover reveals evidence of genetic changes that may have contribution to their evolution.

The first genome sequence of the diamondback moth (DBM, 339 Mb) has been published, and this insect is the most destructive pest of brassica crops. This work shows the genetic and molecular bases for the evolutionary success of this worldwide herbivore, and offers insect insights into insect adaptation to host plant and opens new ways for more sustainable pest management.

The
Triticum urartu (AA) draft genome sequence (4.94 Gb) provides a diploid reference for analysis of polyploid wheat genomes and is a valuable resource for the evolution, domestication, and genetic improvement of wheat.

The
Aegilops tauschii draft genome (4.36 Gb) provides novel insights into its role in enabling environmental adaptation of common wheat and in defining the large and complicated genomes of wheat species.

The panda genome was the first genome completely sequenced by next generation sequencing platform alone. It provides clues to the understanding of everything from the panda’s strict bamboo diet to it’s genetic diversity. It may also aid in the panda conservation in the future.
To provide better quality service for our customers, we offer two types of plant and animal de novo sequencing services, X bio and Intelligen.
X bio, which includes genome survey, sequencing, and genome assembly, is best for those customers with some bioinformatics knowledge and the ability to conduct further analysis of the assembly results themselves.
Intelligen is suitable for those customers with greater needs for bioinformatics analysis, and we can provide end-to-end solutions for your specific research needs. This service includes what is offered in X bio plus gene annotation, evolution analysis, and any other personalized analysis.
Workflow:
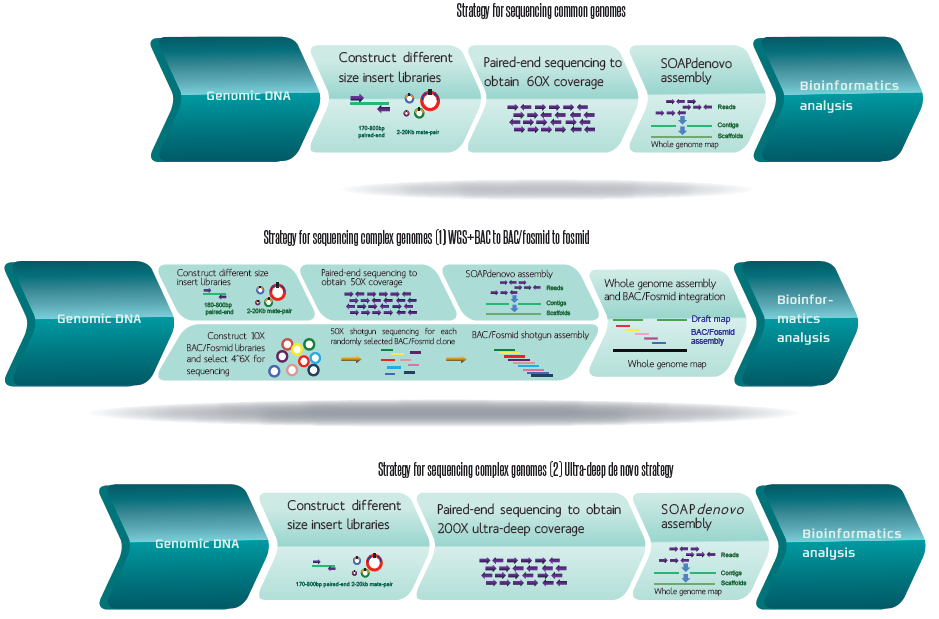
Research Strategies:
- Library construction strategies:
- Paired-end library construction strategy with insert size of 170 bp, 500 bp, and 800 bp
- Long-span mate-pair library construction strategy with insert size of 2 kb, 5 kb, 10 kb, 20 kb, and 40 kb
- Sequencing strategy:
- The average sequence depth is greater than 80X.
- Sequencing strategy of pair end library: 91PE or 101PE sequencing
- Sequencing strategy of mate-pair library: 50PE or 91PE sequencing
- Sequencing using PacBio’s single molecule real-time (SMRT) technology is also available for specific research needs.
Bioinformatics:
X bio -- Best for those customers with some bioinformatics knowledge
| Genome survey |
- Data filtering
- K-mer depth distribution analysis and genome size estimation
- Genome heterozygous rate estimation
- Preliminary assembly
|
| Genome assembly |
- Genome assembly
- GC-Depth distribution analysis
- GC-Content distribution analysis
- Sequencing depth analysis
|
Intelligen -- Best for those customers with greater needs for bioinformatics analysis
| Genome survey |
- Data filtering
- K-mer depth distribution analysis and genome size estimation
- Genome heterozygous rate estimation
- Preliminary assembly
|
| Genome assembly |
- Genome assembly
- GC-Depth distribution analysis
- GC-Content distribution analysis
- Sequencing depth analysis
- Evaluation of coverage of autosomal chromosome (BAC or Fosmid sequence should be provided)
- Evaluation of coverage of interested genes (EST or transcriptome data should be provided)
|
| Annotation |
- Repeat annotation
- Gene prediction
- Gene function annotation
- ncRNA annotation
|
| Evolution analysis |
- Genome map with GC skew and annotation
- Gene family identification (animal: TreeFam; plant: OrthoMCL)
- Phylogenetic analysis
- Estimation of species divergence time
- Genomic island prediction
- Genome-wide synteny analysis
- Segmental duplication analysis (animal: WGD; plant: WGAC)
|
Sample Requirements
- Sample quantity required (single pair):
- Short-insert libraries: ≥3 µg
- 2 kb large-insert libraries: ≥20 µg
- 5 kb-6 kb large-insert libraries: ≥20 µg
- 10 kb large-insert libraries: ≥30 µg
- 20 kb and 40 kb large-insert libraries: ≥60 µg
Note: The total quantity of sample required is also determined by the experimental strategy, as well as the type and number of libraries to be constructed.
- Sample concentration:
- Short-insert libraries: ≥30 ng/ µL
- Large-insert libraries: ≥133 ng/ µL
- Sample purity: OD260/280= 1.8-2.0
Turnaround Time:
| Services |
X bio |
Intelligen – Common genome |
Intelligen – Complex genome |
| Turnaround time |
4–9 months (depending on genome complexity) |
6 months |
1 year |
Completion Criteria
| Species |
Completion Indicator |
| Birds , Mammals (except Chiroptera) |
Contig N50 ≥ 30 kb; Scaffold N50 ≥ 2 Mb |
| Plants |
Contig N50 ≥ 30 kb; Scaffold N50 ≥ 800 kb |
| Complex genome |
Contig N50 ≥ 20 kb; Scaffold N50 ≥ 300 kb |
| Others |
Contig N50 ≥ 20 kb; Scaffold N50 ≥ 600 kb |

 de novo genome sequencing is used to sequence uncharacterized genomes where there is no reference sequence available, or known genomes where significant structural variation is expected. A detailed genetic analysis of an organism is possible only after de novo sequencing has been performed. To date, BGI Tech has sequenced 656 plant and animal reference genomes. The completed projects include rice, cucumber, potato, wheat, silkworm, panda, ant, oyster, minke whale, and so on.
de novo genome sequencing is used to sequence uncharacterized genomes where there is no reference sequence available, or known genomes where significant structural variation is expected. A detailed genetic analysis of an organism is possible only after de novo sequencing has been performed. To date, BGI Tech has sequenced 656 plant and animal reference genomes. The completed projects include rice, cucumber, potato, wheat, silkworm, panda, ant, oyster, minke whale, and so on.
 Comparative analysis of Fruit bat Pteropus alecto and insectivorous Myotis davidii genomes (~ 2 Gb) provides insight into the phylogenetic placement of bats, and moreover reveals evidence of genetic changes that may have contribution to their evolution.
Comparative analysis of Fruit bat Pteropus alecto and insectivorous Myotis davidii genomes (~ 2 Gb) provides insight into the phylogenetic placement of bats, and moreover reveals evidence of genetic changes that may have contribution to their evolution.
 The first genome sequence of the diamondback moth (DBM, 339 Mb) has been published, and this insect is the most destructive pest of brassica crops. This work shows the genetic and molecular bases for the evolutionary success of this worldwide herbivore, and offers insect insights into insect adaptation to host plant and opens new ways for more sustainable pest management.
The first genome sequence of the diamondback moth (DBM, 339 Mb) has been published, and this insect is the most destructive pest of brassica crops. This work shows the genetic and molecular bases for the evolutionary success of this worldwide herbivore, and offers insect insights into insect adaptation to host plant and opens new ways for more sustainable pest management.
 The Triticum urartu (AA) draft genome sequence (4.94 Gb) provides a diploid reference for analysis of polyploid wheat genomes and is a valuable resource for the evolution, domestication, and genetic improvement of wheat.
The Triticum urartu (AA) draft genome sequence (4.94 Gb) provides a diploid reference for analysis of polyploid wheat genomes and is a valuable resource for the evolution, domestication, and genetic improvement of wheat.
 The Aegilops tauschii draft genome (4.36 Gb) provides novel insights into its role in enabling environmental adaptation of common wheat and in defining the large and complicated genomes of wheat species.
The Aegilops tauschii draft genome (4.36 Gb) provides novel insights into its role in enabling environmental adaptation of common wheat and in defining the large and complicated genomes of wheat species.
 The panda genome was the first genome completely sequenced by next generation sequencing platform alone. It provides clues to the understanding of everything from the panda’s strict bamboo diet to it’s genetic diversity. It may also aid in the panda conservation in the future.
The panda genome was the first genome completely sequenced by next generation sequencing platform alone. It provides clues to the understanding of everything from the panda’s strict bamboo diet to it’s genetic diversity. It may also aid in the panda conservation in the future.


